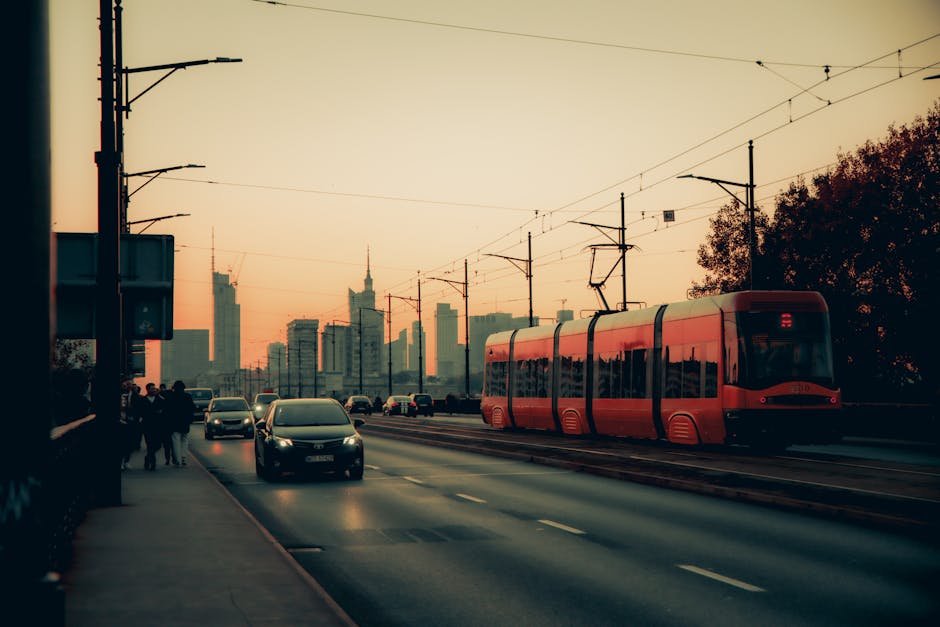
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman stunned the AI community by publicly admitting that their flagship GPT-5 model debuted “way dumber” than intended due to a critical technical failure during rollout. After a severe autoswitcher malfunction caused unexpected performance degradation, Altman stated fixes are now deploying immediately with tangible improvements expected. This unprecedented transparency highlights the hidden complexities of large-scale artificial intelligence deployment, even for industry leaders.
Technical Breakdown and Corrective Actions
The core issue stemmed from flawed model routing infrastructure where the “decision boundary” logic failed to properly direct queries. Altman confirmed immediate adjustments to prioritize smarter model selection and introduced query-level transparency – users will now see exactly which AI version (GPT-5 or legacy models) generates each response.
Scaling Challenges and Critical Mitigations
Operational pressure amplified the incident as API traffic doubled within 24 hours of GPT-5’s release. To manage transition impacts, OpenAI is:
- Maintaining access to GPT-4 Turbo via Settings
- Temporarily increasing rate limits for ChatGPT Plus subscribers
Source: Pexels Image
Performance Potential vs. Initial Reality
The admission contrasted sharply with OpenAI’s launch claims, which touted record-breaking results in math competitions, advanced coding benchmarks, and multilingual applications. While GPT-5 Pro demonstrated improved reasoning capacity in controlled tests, workflow disruption dominated early adoption reports. Developers on technical forums and Hacker News threads highlighted latency spikes and inconsistent agentic tool use during the unstable rollout.
Path Forward for Next-Gen AI Models
Despite turbulence, GPT-5’s architecture remains engineered for breakthroughs in chain-of-thought reasoning and specialized domains. If Altman’s routing corrections succeed, generative AI’s trajectory may stabilize quickly — but this episode serves as a critical case study on scaling cutting-edge machine learning systems under real-world demand.